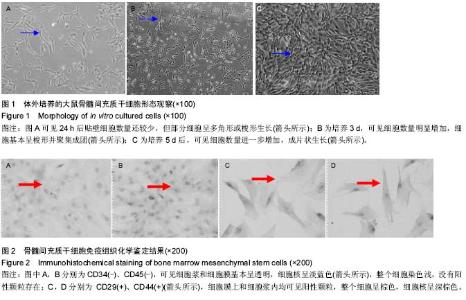
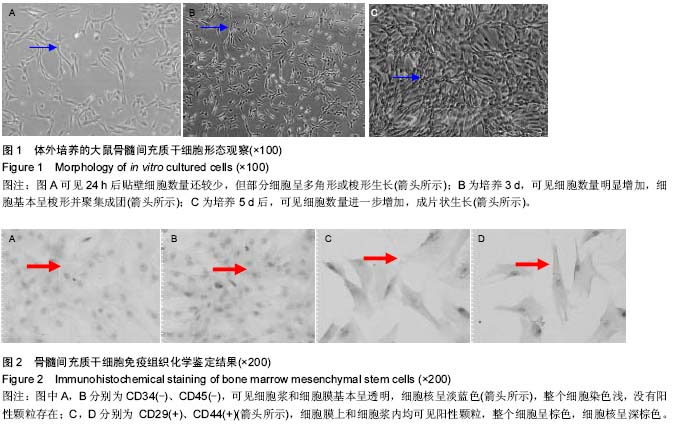
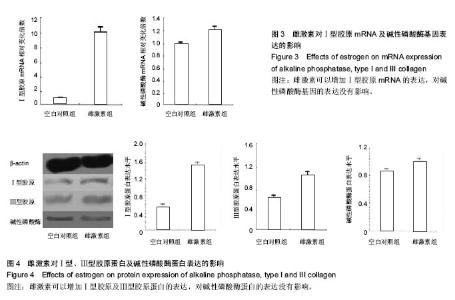
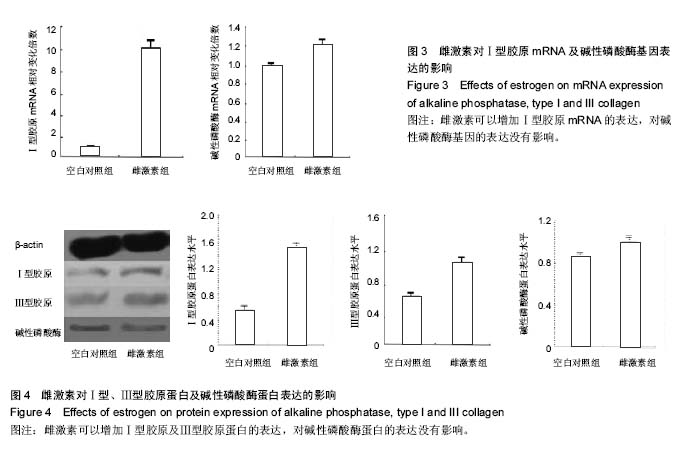
| [1] Panzarini SR, Gulinelli JL, Poi WR, et al.Treatment of root surface in delayed tooth replantation: a review of literature. Dental Traumatology.2008;24(3):277-282.
[2] Kramer P,Nares S,Kramer S,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells acquire characteristics of cells in the periodontal ligament in vitro. J Dent Res. 2004;83(1):27-34.
[3] 代媛媛, 原工杰, 余桂戎, 等. 间接共培养诱导大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向牙周膜成纤维样细胞分化[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志, 2010, 26(5):764-768.
[4] Kim K,Lee C,Kim B,et al.Anatomically shaped tooth and periodontal regeneration by cell homing. J Dent Res. 2010;89(8):842-847.
[5] 杜令倩. 趋化因子SDF-1对人牙周膜干细胞增殖、迁移及分化的影响[D]. 济南: 山东大学,2011.
[6] Kucia M, Dawn B, Hunt G, et al. Cells expressing early cardiac markers reside in the bone marrow and are mobilized into the peripheral blood after myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 2004;95(12):1191-1199.
[7] Horuk R.Physiology: Chemokines beyond inflammation. Nature.1998;393(6685):524-525.
[8] Zou YR, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, et al. Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development.Nature.1998; 393(6685): 595-599.
[9] Ratajczak MZ, Majka M, Kucia M, et al. Expression of Functional CXCR4 by Muscle Satellite Cells and Secretion of SDF-1 by Muscle-Derived Fibroblasts is Associated with the Presence of Both Muscle Progenitors in Bone Marrow and Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Cells in Muscles.Stem Cells.2003; 21(3):363-371.
[10] Yamaguchi JI, Kusano KF, Masuo O, et al. Stromal cell–derived factor-1 effects on ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cell recruitment for ischemic neovascularization. Circulation.2003;107(9): 1322-1328.
[11] Shirozu M, Nakano T, Inazawa J, et al. Structure and chromosomal localization of the human stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF1) gene. Genomics.1995; 28(3):495-500.
[12] Feng Y, Broder CC, Kennedy PE,et al. HIV-1 entry cofactor: functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science.1996; 272(5263):872-877.
[13] Ji JF, Dheen ST, Kumar SD, et al. Expressions of cytokines and chemokines in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve after right vagotomy. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;142(1):47-57.
[14] Shimode K,Iwasaki N,Majima T,et al.Local Upregulation of Stromal Cell–Derived Factor-1 After Ligament Injuries Enhances Homing Rate of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells in Rats. Tissue Engineering Part A.2009; 15(8):2277-2284.
[15] Kannus P, Parkkari J, Järvinen T, et al. Basic science and clinical studies coincide: active treatment approach is needed after a sports injury. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2003;13(3):150-154.
[16] Hong F, Tuyama A, Lee TF, et al. Hepatic stellate cells express functional CXCR4: Role in stromal cell-derived factor-1α-mediated stellate cell activation. Hepatology. 2009;49(6):2055-2067.
[17] Lin D, Kenny D, Barrett E, et al. Storage conditions of avulsed teeth affect the phenotype of cultured human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 2000; 35(1):42-50.
[18] Kato C, Kojima T, Komaki M, et al. S100A4 inhibition by RNAi up-regulates osteoblast related genes in periodontal ligament cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326(1):147-153.
[19] Woo SL, Hildebrand K, Watanabe N, et al.Tissue engineering of ligament and tendon healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;367:S312-S323.
[20] Agarwal C, Britton ZT, Alaseirlis DA, et al.Healing and normal fibroblasts exhibit differential proliferation, collagen production, α-SMA expression, and contraction. Ann Biomed Eng. 2006 ;34(4):653-659.
[21] Alborzi A, Mac K, Glackin CA,et al.Endochondral and intramembranous fetal bone development: osteoblastic cell proliferation, and expression of alkaline phosphatase, m-twist, and histone H4. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1996;16(2):94.
[22] 程远,曾照芳,朱俊.人牙龈成纤维细胞与牙周膜细胞的生物活性[J]. 生物信息学, 2009, 7(1):32-36.
[23] Tan Z, Zhao Q, Gong P, et al. Research on promoting periodontal regeneration with human basic fibroblast growth factor-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cell gene therapy. Cytotherapy. 2009; 11(3): 317-325.
[24] 罗杰,谭震.牙周再生术治疗中微环境的构建和维护[J].现代临床医学, 2009, 35(1):3-5.
[25] Ding G, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. Allogeneic periodontal ligament stem cell therapy for periodontitis in swine. Stem Cells.2010;28(10):1829-1838.
[26] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood.2005;105(4):1815-1822.
[27] 张蕾,陈槐卿. 与韧带成纤维细胞间接共培养对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞胶原蛋白和韧粘素-C表达的影响[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2007, 24(4): 846-851.
[28] Kushida T, Inaba M, Hisha H, et al. Intra–bone marrow injection of allogeneic bone marrow cells: a powerful new strategy for treatment of intractable autoimmune diseases in MRL/lpr mice. Blood. 2001;97(10): 3292-3299. |